Long Waves: The Power of Innovation Cycles
Aug 9, 2024 • 8 min read
Have you thought how much the available technologies dictate how we live? Here are some challenges to think about next time you find yourself in the following situations:
- In your car on a long-distance trip: how much it took a person to get to your destination 200 years ago? How many of the people could afford that?
- In the laundry room: how much time you don’t spend washing and drying your clothes?
- Calling a friend on the phone: How much did communication change after the cellphones replaced the landlines?
Understanding the technology waves is crucial for founders and product leaders looking to stay ahead of the curve.
In this blog post, we'll explore:
- the history of innovation cycles,
- their impact on business growth and product development,
- how you can harness these cycles to get to market success,
- the next great thing you can build.
What Are Innovation Cycles?
Innovation cycles are periods of technological and economic change that disrupt existing markets and create innovative products. Joseph Schumpeter was an economist who coined "creative destruction" in 1942. It describes how these cycles lead to the rise and fall of industries.
The Six Waves of Evolution of Innovation
First Wave: Water Power and Textiles
The first wave of innovation began in the late 18th century with the advent of water power and textile manufacturing. This period saw the rise of factories and the transformation of urban landscapes. Water-powered mills revolutionized the production of paper, textile, and iron goods, leading to significant economic growth.
Second Wave: Steam and Rail
Between 1845 and 1900, the second wave was driven by steam power and the rail industry. Railways connected cities, boosted trade, and spurred industrial growth. This era also saw advancements in steel production, further fueling economic expansion.
Third Wave: Electricity and Chemicals
The third wave was from the late 19th to the early 20th century. It was marked by the wide adoption of electricity and the emergence of chemical industries. Innovations like the incandescent light bulb and telephone transformed communication and improved quality of life.
Fourth Wave: Automobiles and Aviation
The fourth wave spanned the early to mid-20th century. It brought the mass production of automobiles and the emergence of aviation. Henry Ford's assembly line transformed manufacturing processes, while airplanes connected the world like never before.
Fifth Wave: Digital Networks and New Media
In the late 20th century, the fifth wave was characterized by the rise of computers and digital networks. The internet changed information sharing, communication, and commerce, giving birth to the digital age we live in today.
Sixth Wave: Artificial Intelligence and Clean Tech
We are currently in the sixth wave of innovation, driven by artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and clean tech. These technologies will redefine industries, improve efficiency, and address global challenges like climate change.
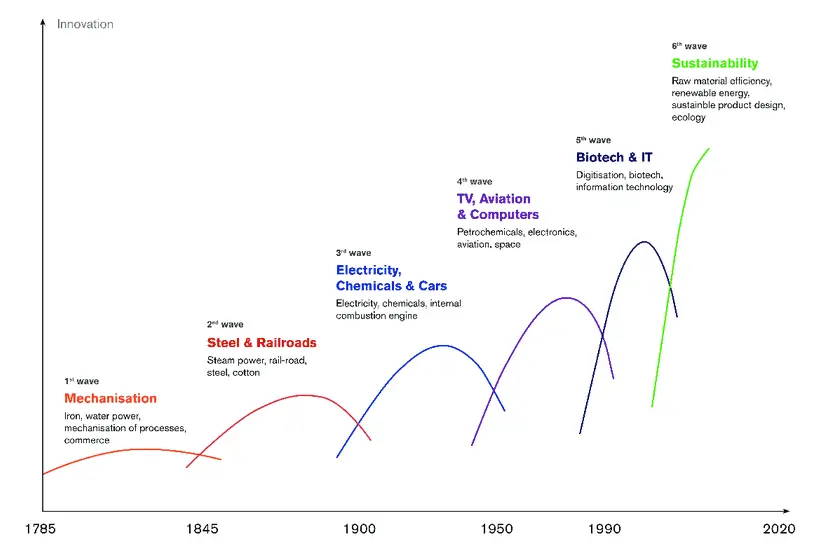 (source: Evolution of Technology and Technology Governance - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate.)
(source: Evolution of Technology and Technology Governance - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate.)
Why Innovation Cycles Matter for Businesses
Understanding innovation cycles is essential to build a thriving and enduring business in a constantly evolving environment. Here's why:
Staying Ahead of the Curve
By recognizing the stages of innovation cycles, businesses can anticipate market shifts and adapt accordingly. This proactive approach can help companies remain competitive and leverage emerging opportunities.
This is the key to distinguishing themselves from competitors with unfair advantages and attracting customers with unique value propositions.
Driving Efficiency and Growth
Innovation cycles often bring about new technologies to enhance efficiency and drive growth. For example, AI-powered tools can streamline operations, improve decision-making, and optimize resource allocation. Clean technologies reduce the cost of operations and dependencies on finite resources.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
Staying on top of emerging innovations allows businesses to meet customer needs better. Adopting new technologies and practices can improve companies' products and services, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The Innovation Lifecycle
The book “Crossing the Chasm” defines the different phases of innovation adoption using various psychographic profiles. The theory behind the book explains the mechanism for a discontinuous innovation to gain traction and become a mainstream product. However, using the same model for innovation adoption can also help understand the wave of technology.
Understanding how innovations are adopted can help businesses strategize effectively. The innovation adoption curve consists of five phases:
Innovators
Innovators are the first to adopt new technologies. These risk-takers are willing to experiment and invest in unproven solutions, setting the stage for broader adoption.
Early Adopters
Early adopters follow closely behind innovators. They are often influential market leaders who recognize innovations' potential and quickly integrate them into their operations. To gain an advantage, early adopters are open to products not ready for prime time.
Early Majority
The early majority represents a significant portion of the market. These adopters wait until innovations have been proven and tested before committing. They look for benefits from well-established solutions.
Late Majority
The late majority is more cautious, adopting innovations only after they have become mainstream. These businesses prefer to minimize risk and follow established best practices.
Laggards
Laggards are the last to adopt new technologies. They may resist change due to skepticism or lack of resources, eventually adopting innovations when they become inevitable.
Adapting your product or service to each customer segment will help you meet that customer's needs and extract the maximum benefit.
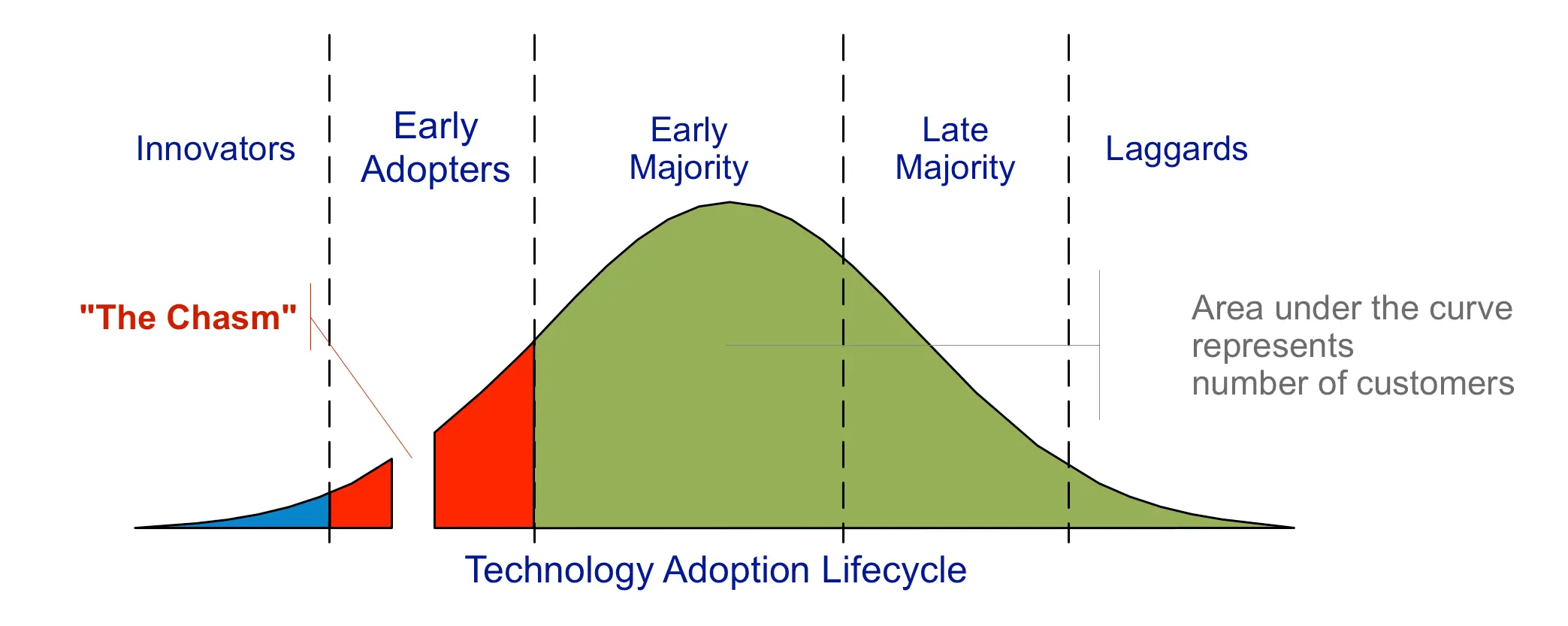 (source: Wikimedia)
(source: Wikimedia)
Implementing Innovation in Your Business
To successfully implement innovation in your business, consider the following steps:
Conduct Market Research
Conduct thorough market research to identify emerging trends and technologies relevant to your industry. This will help you understand how innovation cycles will likely impact your market. The Icanpreneur platform can help you conduct customer problem interviews following the best industry practices.
Develop a Clear Strategy
Develop a clear strategy for integrating new technologies into your business. This should include setting specific goals, allocating resources, and establishing timelines for implementation.
Foster a Culture of Innovation
Encourage a culture of innovation within your organization. You can achieve such a culture by:
- promoting creativity,
- supporting risk-taking,
- providing opportunities.
Leverage Customer Feedback
Gather and analyze customer feedback to identify areas where innovation can enhance your products and services. This will help you stay attuned to customer needs and preferences, ensuring your innovations are well-received.
Collaborate with Industry Experts
Collaborate with industry experts, research institutions, and technology providers to stay informed about the latest advancements. Networking will help you access valuable insights and resources for successful innovation.
We prepared a list of 15 YouTube channels about entrepreneurship that you can follow to stay on top of the news. The Icanpreneur community is another great way to connect with like-minded peers.
There are a few challenges to keep in mind when implementing disruptive changes:
- Resistance to change: employees or customers may resist the proposed change driven by various fears.
- Limited resources: disruptive innovations usually require significant resources, time, and talent investments.
- Managing risks: Innovations are usually high-risk, high-return activities, and you must handle risks accordingly.
Real-World Examples of Successful Innovation
Look at the 10 Lean Canvas for innovative examples from companies like Tesla, Netflix, and Amazon.
Future Trends in Innovation Cycles
Several trends are likely to shape the future of innovation cycles moving forward:
Quantum Computing and AI
Quantum computing and AI together can solve new class of problems that couldn't be solved before. These technologies could lead to breakthroughs in fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and climate modeling.
Biotech and Longevity
Gene editing and personalized medicine are set to transform healthcare. Biotech innovations will enable more effective treatments, early disease detection, and improved patient outcomes.
One of humanity’s greatest quests is the search for eternal life. Science has shown the path to longer and healthier lives, and technological innovation is already happening. However, this quest comes with significant moral and ethical questions that we have yet to answer.
Sustainable Technologies and Clean Tech
With growing concerns about climate change, sustainable technologies will be crucial in addressing environmental challenges. Innovations in renewable energy, carbon capture, and circular economy practices will drive the transition to a more sustainable future.
Due to these influencing factors, the electrical industry is about to undergo major changes in production, transportation, and consumption.
Conclusion
Innovation cycles have shaped history and driven economic growth and societal progress. By understanding these cycles and strategically implementing new technologies, businesses can stay ahead of the curve, enhance efficiency, and achieve long-term success.
Author
Product @ Icanpreneur. Coursera instructor, Guest Lecturer @ Product School and Telerik Academy. Angel Investor. Product manager with deep experience in building innovative products from zero to millions of users.
