Business Model Innovation: Everything You Need to Know
Jul 19, 2024 • 12 min read
What is Business Model Innovation?
Business Model Innovation is the process of reimagining the relationships between the different components of your business model to create a better product or service for your customers.
Business Model Innovation is usually related to discontinuous innovation, as profound changes cannot be delivered through incremental improvements.
Why Is Business Model Innovation Important?
Innovative business models are often highly disruptive to competitors and put the company in a strong position. There are multiple factors leading to that effect that often magnify each other.
Business model innovation is crucial for companies, as demonstrated by the example of Coursera (NYSE:COUR), an EdTech company. Coursera operates a marketplace where educational content from top institutions is directly accessible to a global audience of learners, enterprises, and public organizations. Unlike competitors that typically focus on specific markets or independently source content. Coursera collaborates with educational partners to offer various stackable courses, professional certificates, and even degrees alongside traditional MOOCs.
- Agility to Market Changes
Business Model Innovations often arise from changes in the business environment. By creating a new business model, companies can respond to those changes and adapt quicker than competitors.
Coursera's flexible business model enables them to offer a new service to campuses in a matter of weeks during the coronavirus outbreak. Coursera managed to spin up a new product for a brand new customer segment would typically take months, if not years. They were able to onboard universities that had to switch from onsite to online teaching methods in a matter of weeks. This provided strong tailwinds for the company caused by market shifts in the educational space.
- Increased Customer Value
Creating a new business model frequently unlocks the ability to deliver value to customers in ways that were previously impossible or difficult.
By transitioning from human translations reliant on contracts and community contributions to machine-based translations, Coursera expanded its online education offerings into previously inaccessible markets due to high localization costs.
- Competitive Advantage
Coursera’s business model represents a three-sided marketplace for educators (university and industry partners), learners (consumers, businesses, and public organizations), and employers (companies looking to hire talent).
This model gives the company a unique advantage by tapping into multiple markets and mutually reinforcing each other.
It creates unique value propositions that are hard to be replicated by competitors like:
- Get a world-class degree from the comfort of your home
- Provide a new revenue stream for tier 2 universities by making them available to learners from all around the world
The unique business model also creates unfair advantages that are hard to replicate, like “Content from world-class educational providers.”
- Revenue Growth and Profitability
As a consequence of all the factors above, companies with innovative business models often see strong revenue growth and profitability delivered through new revenue streams, operational efficiency, and reduced costs.
Diversifying the business model also leads to a lower risk of external factors affecting its bottom line. Take a look at data from multiple studies on the topic of business model innovation:

Now that we understand the importance of looking for business model innovation opportunities, what are its prerequisites?
Must-haves for Business Model Innovation
Customer Benefits
Innovation in any form starts by answering the question, “What is it that customer’s value that is currently underserved?” At the end of the day, a change in the business model is innovation only if it’s valuable for a significant enough customer segment. Otherwise, it’s noise at best and a complete disaster at worst.
Conducting thorough customer problem research can help you understand your customers' problems deeply. One of the best ways to execute such research is to conduct customer problem interviews, which allow you to study your potential customers' experiences and hear about the current gaps of the solution they are using.
Our platform streamlines the customer problem interview process for entrepreneurs and product builders by facilitating it end to end, from preparation and scheduling to capturing insights with confidence from the conversations.
Risks Analysis
Fundamental changes in the business model come with certain risks. Some of them might be:
- Confusing existing customers
- Failing to attract new customers
- Upsetting partners and vendors
- Demotivating employees
Depending on the specific situation, a risk analysis with a contingency plan is needed to ensure your existing business is not at risk.
Key Resources
What assets do you have that put you uniquely positioned to pursue a different business model? These might be:
- Data: Quality data can be a valuable advantage, especially in the AI and IoT-dominated world.
- Skills: Does your expertise contribute to implementing the new business model?
- Experience: Previous experience, especially from different industries, can be transferable in amazing ways. It can help you spot business opportunities in the business model missed by the other players solely focused on their market.
Partners
Who do you need to partner with that will put your company in a unique position to create a new business model? Amazon turns from a retailer to a marketplace for other retailers, allowing the company to move away from managing a vast inventory and distribute that burden to its many vendors.
Now, let’s review the different types of innovation that should be considered.
Types of Business Model Innovation
The “Reinventing Your Business Model” article on Harvard Business Review defines the different types of business model innovation:
Automation Enabled
As with the machine translation examples above, automating a task that was previously manually done by humans opens up opportunities. It is one way to enhance a business model, and this type of innovation is often powered by some kind of technological breakthrough.
Brokerage
Delivering value by being the middleman between two parties that otherwise experience severe friction. That’s the example of eBay, which aims to facilitate the process of person-to-person sales through bidding.
Packaging
Create packages of products that bring more value to customers together than separately. This often is a perceived value on the consumer’s end rather than actual value gain.
Crowdsourcing
This is the famous example of Wikipedia, which became the biggest source of credible information, completely destroying the encyclopedia market. The key here is to create the environment for the user base to build the product in exchange for something else they value (which might be completely altruistic, as in the case of Wikipedia).
Data -> Value
Some companies turn their data possession into value, which creates a new business model that was previously unseen. Waze is an example of crowdsourcing the data-gathering process to create brand-new value.
Digital Platforms
Turning a traditional seller -> buyer relationship into a marketplace where a digital platform mandates the relationship between the two personas is another path to creating new business models. Etsy is an excellent example of a digital platform that facilitates the connection between artists and craftsmen, with consumers.
Cutting the Middleman
Eliminating middlemen is another opportunity to create a new business model. Tesla took that approach when it decided not to use dealerships like most car manufacturers and to sell directly to consumers. This matters because it allows the company to own the end-to-end relationship, focus on quality, reduce regular service visits to 0, etc.
Share Assets
In other words - The Shared Economy! Business models in that area allow one party to monetize by sharing ownership of expensive assets with others. Airbnb and Uber have built on this approach.
Freemium
Offering a product for free up to certain limitations was revolutionary in the 2010s with the advent of cloud technologies and SaaS. When implemented well, such models create a strong sales funnel that later converts freemium users to paid premium features or allows them to continue using the product after certain usage-based limits are hit.
Low-touch - low-cost
Low-cost airlines employ a business model of reducing the level of service for the benefit of lower prices, which is currently putting a lot of pressure on traditional companies. Driven by Ryanair's aggressive low-cost approach, many traditional airlines in Europe are forced to follow their approach to remain relevant.
Pay as you go
Pay as you go, or PAYG, is a business model that allows users to pay only for the amount of product or service they actually consume. Cloud providers used that approach to democratize access to computational resources.
Standardization
Streamlining a previously complicated, more expensive service is another way to provide a better product for consumers. While the complexity might be valuable for a certain part of the market, there could be a segment that doesn’t care about that and would trade it for other benefits like lower prices, better performance, or higher quality.
Club Memberships
Offering a club membership as a standalone product or as a complementary product to an existing product is another strategy to create a new revenue stream. Again, many low-cost companies offer membership to offer even lower prices, gaining customer loyalty in turn.
Best Practices to Uncover New Business Models
What are the different directions in which you can explore the opportunities for an innovative business model?
- Move risk
If a specific risk is involved in the current business models, one option to consider is moving that risk to a different party in a better position to handle it. An example is Amazon's dropshipping model, which allows them to mitigate the risk of managing enormous inventory by moving it to vendors, each of which handles a much smaller risk individually.
Another way to move risk is from the consumer to your company. Car subscription services take this approach, removing the hassles of drivers owning a car and dealing with all associated risks with it. In exchange for a service fee, you can rely on having a car.
- Move decision making
LEGO Ideas is an example of moving decision-making to a party in a better position to make better decisions. Instead of the LEGO designers making the final call on what sets to move to production, consumers vote for ideas.
- Move incentives
In India, seven founders decided to create a cooperative in which women roll papadams (traditional food). The interesting story is that every woman is, in fact, an equal partner as opposed to an employee, leading to higher engagement and commitment to the organization’s operations.
- Move load
The next strategy for innovating on the business model level is to shift the load of operations or financials to a different party. In the case of Airbnb, the load of managing the accommodation is transferred from the company (like hotels) to the hosts.
- Reduce value in exchange for other benefits
Low-cost airlines operate on the premise that additional service on board brings little value on short—to mid-distance flights compared to the expenses needed to deliver them. So, travelers are happy to sacrifice the sandwich for a cheaper ticket, which frees time for the cabin crew to create new revenue streams like selling goods.
- Multisided platforms
Turning from a product to a multisided platform (or marketplace) is another powerful strategy for creating an innovative business model. This strategy piggybacks on one or many of the previous strategies, allowing the company to significantly scale its operations and market.
Key Components of Business Model Innovation
Let’s explore seven properties of a business model based on which we will evaluate the potential for a challenger to displace an incumbent.
Tailored Experience
Tailored experience is the potential of a new business model to provide consumers with more personalized and adapted products or services based on their preferences and needs.
Circular Resource Utilization
Circular resource utilization is the ability of the model to reuse resources used to serve one customer to serve others.
Asset Sharing
This is the manifestation of the sharing economy. Does the model have the ability to share assets across different parties of the business model?
Consumption-based Pricing
Does the business model offer pricing based on utilizing the product or service purchased?
Partnership and Cooperation
Is the updated model fostering stronger cooperation and partnership between different players in the model?
Flexibility and Responsiveness
This is the ability of the model to adapt to changes in different parameters, such as demand, supply, cost of goods, etc.
Technology Innovation Tailwinds
Technology innovations don’t create new models on their own, but they open a window of opportunity for companies to realize the potential of technology to improve a problem significantly.
Using these components, we can create a framework to compare two different companies (a challenger and an incumbent), we will assign 3 points on all components for the incumbent as a baseline and compare the challenger against it.
- Assign 4 or 5 points to the challenger who is doing slightly better or extremely better, respectively
- Assign 2 or 1 point if the challenger performs worse than the incumbent.
Using the template below, you can visualize the challenger's potential to devour the incumbent if it excels on several of the listed components. At this end of the data, this is just a model, and it matters only if the customers care about it.
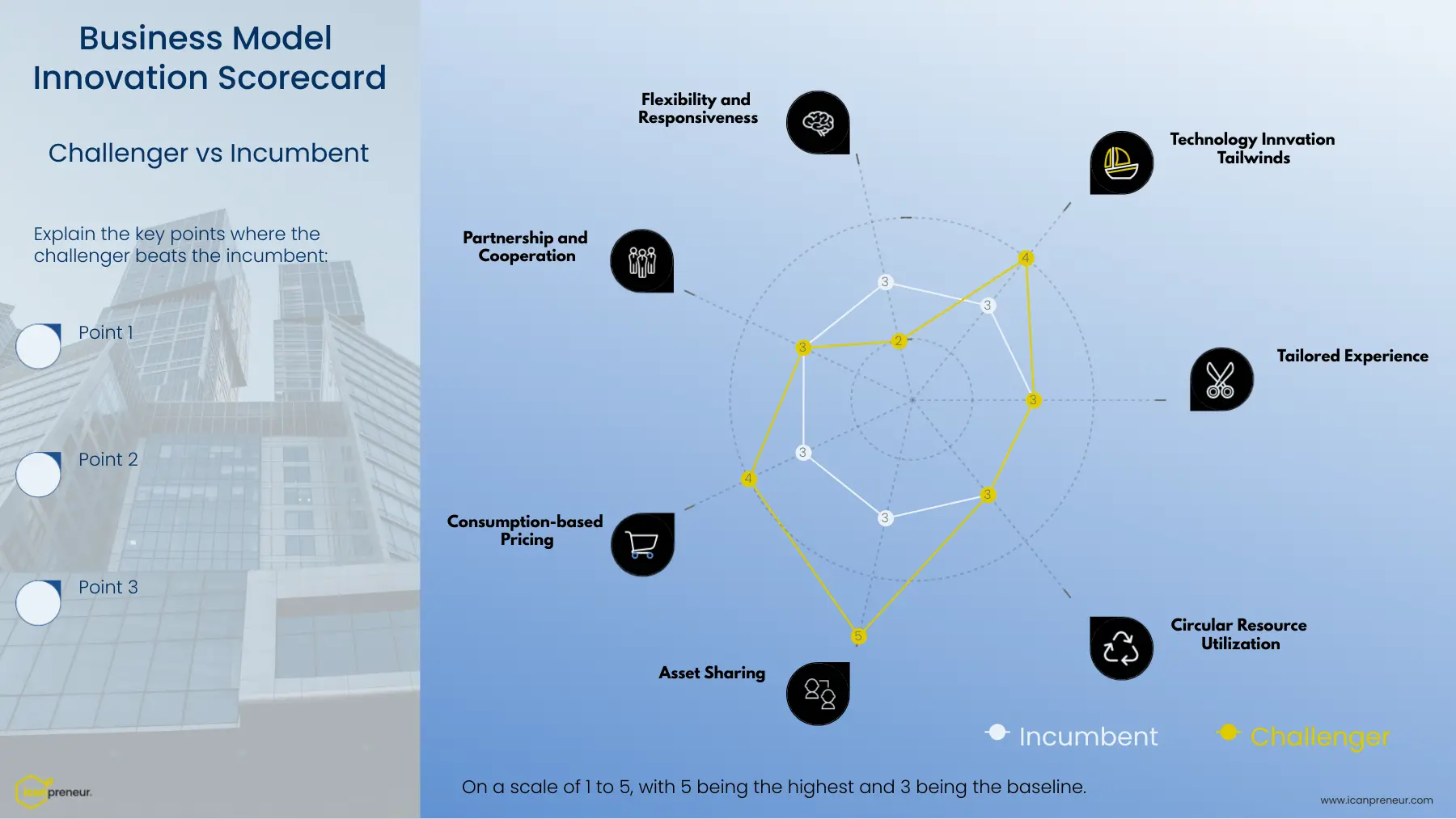
We have prepared a clean version that you can use during your exercises.
Wrap Up
An innovative business model can provide an amazing opportunity for new players to penetrate a market or existing players to retain and increase their differentiation. While it might be a once-in-a-lifetime chance, the potential gains are so significant that no opportunity can be neglected.
Author
Product @ Icanpreneur. Coursera instructor, Guest Lecturer @ Product School and Telerik Academy. Angel Investor. Product manager with deep experience in building innovative products from zero to millions of users.
